#Development of magnetic immunoassay system
Immunoassays which examine the presence or the amount of antibody, a protein of the disease origin made with infection and allergy in the blood, is widely used for a diagnosis of a disease. An antibody is detected by using a marker modified by the protein which combines with only a specific antibody and measuring a signal from the marker. An optical marker such as a fluorescent material is used at present. Magnetic immunoassay using a magnetic marker with magnetic nanoparticles has attracted attention as an alternative method. In magnetic immunoassay, bound and unbound markers can be distinguished by utilizing the difference in Brownian rotary motion. Therefore the process to wash out excess markers becomes unnecessary, and a quick check becomes possible. Development toward a check of whole blood and a check in the body is also expected because the sample in which light doesn't penetrate through can be checked. SUSTERA has participated in a JST S-innovation project and has been developing a magnetic immunoassay system with ultrahigh sensitivity. It has been demonstrated that very small amount of antibody of atto-mole (10-18 mole) level can be detected by using an HTS-SQUID sensor.
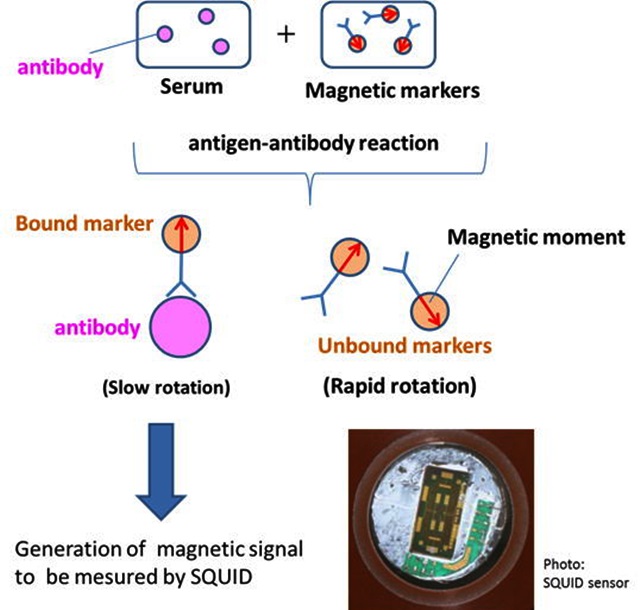
Principle of magnetic immunoassay.
あなたもジンドゥーで無料ホームページを。 無料新規登録は https://jp.jimdo.com から
